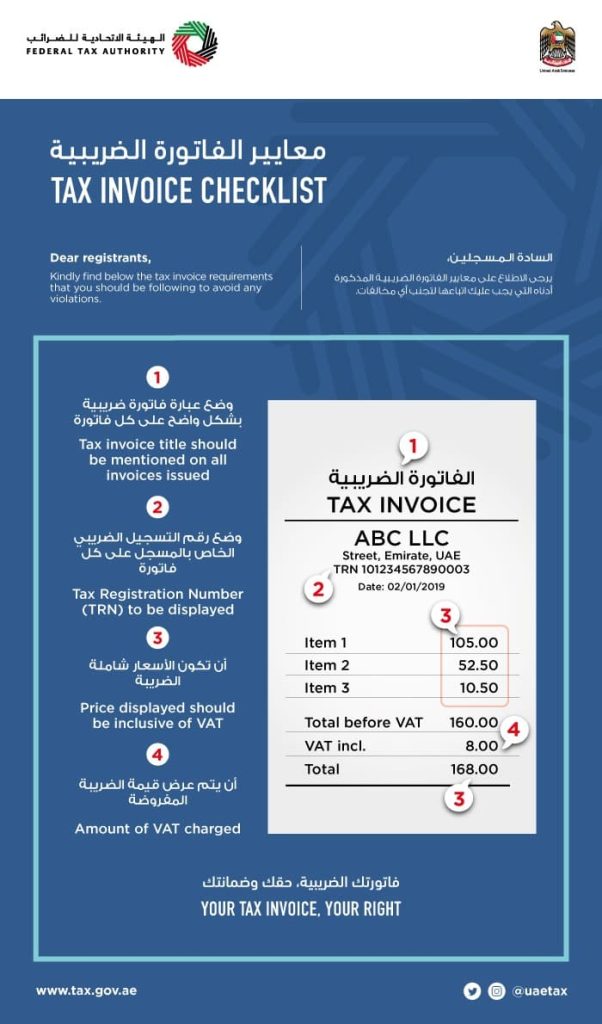
In 2018, the UAE introduced Value-Added Tax (VAT), which is a 5% tax added to most goods and services sold in the country. This includes VAT on courier services, which are an important part of the UAE’s economy. With so many businesses relying on fast and reliable delivery services, understanding how VAT affects courier services is important for both businesses and individuals.
Courier services play a key role in the UAE, helping businesses deliver packages to customers locally and around the world. Whether you’re running an e-commerce business or sending packages across the UAE, knowing how VAT is applied to these services can help you avoid surprises and stay compliant with the law.
So, let’s break down everything you need to know about VAT on courier services in the UAE.
Is VAT Applicable to Courier Services In UAE?
Yes, VAT on courier services in the UAE is typically applied at the standard rate of 5%. Whether you’re using local delivery or sending packages internationally, most courier companies must register for VAT and charge their customers accordingly. However, the way VAT is applied varies for domestic vs. international services.
Domestic vs. International Courier Services VAT in UAE
Domestic Courier Services:
For domestic courier services in the UAE, a 5% VAT is charged to both individuals and businesses. For example, if you’re sending a package from Dubai to Abu Dhabi, the courier company adds 5% VAT to the delivery fee, ensuring that the tax is properly applied.
International Courier Services:
For international courier services in the UAE, the VAT rate is usually zero-rated (0%). Although these services are subject to VAT, no VAT is collected from the customer. This applies when shipping from the UAE to countries like the USA, making international shipments more cost-effective for businesses and consumers.
VAT Exemptions for Courier Services
In the case of international courier services, while they are zero-rated, they are not fully exempt from VAT. A zero-rated service still requires the courier company to report the transaction for VAT purposes, even though no VAT is charged to the customer.
Most courier services, whether domestic or international, are not fully exempt from VAT. International services may qualify for the zero-rated VAT (0%), but they still need to be reported for VAT purposes, while domestic services are taxed at the standard 5%.
How is VAT on Courier Services Calculated?
To calculate VAT on courier services in the UAE, simply add 5% to the delivery fee for domestic shipments. For example, if a courier charges AED 200, an additional AED 10 (5%) VAT is applied, bringing the total to AED 210.
For international deliveries, since the service is zero-rated, no VAT is added to the courier fees. For international shipments, no VAT is added to the courier fee, so if the charge is AED 300, you pay exactly that amount, with no extra taxes.
VAT Registration for Courier Services
Courier service providers must register for VAT if their annual turnover exceeds AED 375,000. Providers earning less than this amount can voluntarily register if their turnover exceeds AED 187,500. Once registered, couriers must charge VAT on eligible services and file regular returns with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA).
VAT Registration Process:
1. Courier service providers must apply for VAT registration through the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) portal.
2. The business will need to provide details such as:
- Company trade license.
- Financial records showing turnover.
- Details of the business activities.
3. Once registered, the business will receive a VAT registration number (TRN), which must be included on all VAT invoices issued to customers.
Failure to register for VAT when required can result in significant penalties. The FTA can impose fines for late registration, failure to charge VAT correctly, or not filing VAT returns on time.
Input Tax Credits for Courier Service Providers
Courier service providers in the UAE can claim input tax credits on VAT paid for business expenses related to their services. These include VAT incurred on fuel, vehicles, packaging materials, and other operational costs.
By claiming input tax credits, courier companies can reduce their VAT liability, allowing them to deduct the VAT paid on these expenses from the VAT collected from customers.
VAT on Imported Goods via Courier
When importing goods into the UAE, VAT is charged on the value of the items, including any customs duties. The courier company typically collects the VAT and remits it to the FTA, ensuring compliance with UAE tax regulations.
However, there may be specific exemptions or reduced VAT rates for certain types of imported goods, depending on their classification and intended use. It’s important to consult with a VAT experts such as Shuraa Tax to determine the correct VAT treatment for imported goods.
VAT on Goods Shipped Within the UAE
For goods shipped within the UAE, VAT is applied both to the value of the goods and the delivery service if the courier company is VAT-registered. The VAT treatment depends on whether the transaction is business-to-business (B2B) or business-to-consumer (B2C):
- B2B Transactions: In B2B transactions, the supplier of the goods is generally responsible for accounting for VAT on the sale of the goods. The courier service provider is not typically required to collect or remit VAT on the value of the goods themselves.
- B2C Transactions: In B2C transactions, the courier service provider is usually responsible for collecting and remitting VAT on the value of the goods, in addition to the delivery fee.
Taxes Applicable to Delivery Services in the UAE
When running a delivery service in the UAE, you may be subject to the following taxes:
1. Value-Added Tax (VAT)
The UAE charges 5% VAT on most goods and services, including domestic courier services, while international shipments are zero-rated for VAT purposes.
2. Customs Duties
Duties apply to goods entering the UAE, typically between 5% and 10%. Couriers may help facilitate customs payments.
3. Corporate Tax
A 9% corporate tax is levied on profits exceeding AED 375,000. Profits below this threshold are not taxed.
4. Excise Tax (If Applicable)
If your delivery service involves the transport of excise goods like tobacco, sugary drinks, or energy drinks, excise tax will apply.
5. Social Security and Insurance Contributions
While the UAE doesn’t have traditional social security taxes, delivery service businesses must ensure their employees have health insurance, which is mandatory under UAE law.
Need Help with VAT on Courier Services? Contact Shuraa Tax Today!
Staying VAT-compliant is crucial for businesses using courier services in the UAE. If you need assistance navigating VAT regulations or have questions about how VAT impacts your business, reach out to Shuraa Tax today! We’ll help ensure you’re fully compliant with all VAT requirements.
If you find all this a bit overwhelming, you’re not alone! Getting professional advice is a smart move. At Shuraa Tax, we offer a range of tax services to help your business meet all VAT requirements easily.
Don’t hesitate to reach out to us today at +971508912062 or info@shuraatax.com and see how we can support you.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does VAT apply to courier services in the UAE?
VAT is applicable to courier services in the UAE at a standard rate of 5% for domestic shipments. For international courier services, the transportation of goods is typically zero-rated, meaning no VAT is charged.
2. What VAT rate applies to importing and exporting goods?
When importing goods into the UAE, a 5% VAT is generally applicable, along with any customs duties. For exported goods, the VAT rate is zero-rated, meaning that no VAT is charged when goods leave the UAE.
3. How does VAT apply to e-commerce businesses using courier services?
E-commerce businesses that use courier services are responsible for charging 5% VAT on domestic shipments. For international deliveries, VAT is typically zero-rated.
4. What are the record-keeping requirements for courier service providers in the UAE?
Courier service providers in the UAE are required to maintain detailed records of their VAT transactions, including invoices, receipts, and payment records. These records should be kept for a period of five years from the end of the tax period in which the transaction occurred.