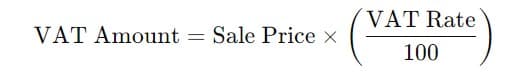Excise tax in UAE was introduced as part of the government’s efforts to reduce the consumption of goods that negatively impact public health and the environment. Implemented in October 2017, this tax targets specific products, such as tobacco, energy drinks, carbonated drinks, sweetened beverages, and electronic smoking devices. The rates are substantial, with a 100% tax on tobacco products, energy drinks, and electronic smoking devices and a 50% tax on carbonated and sweetened beverages.
Businesses must determine the “Excise Price” to calculate UAE excise tax. This price includes the cost of the goods, shipping, and insurance (CIF). Once the Excise Price is established, the tax rate applicable to the product is applied. For example, if a company imports energy drinks with an Excise Price of AED 100, the excise tax would be 100%, resulting in an additional AED 100 tax, making the total cost AED 200.
Businesses dealing with excisable goods must register with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) and regularly file excise tax returns. Failing to adhere to these regulations could result in significant fines. By accurately calculating and paying excise tax, businesses not only avoid penalties but also contribute to the UAE’s broader health and environmental goals.
What is Excise Tax in UAE?
Excise Tax in the UAE is a form of indirect tax levied on specific goods deemed harmful to human health or the environment. It was introduced to discourage the consumption of these goods and generate additional revenue for the government, which can be used to fund public services.
Key Points about Excise Tax in the UAE:
- Introduction Date: The UAE introduced the Excise Tax on October 1, 2017.
- Taxed Goods: The Excise Tax applies to:
- Tobacco products (including e-cigarettes and similar devices): 100% tax rate.
- Energy drinks: 100% tax rate.
- Carbonated drinks: 50% tax rate.
- Sweetened beverages: 50% tax rate (introduced later in December 2019).
- Purpose: The tax aims to reduce the consumption of unhealthy goods, promote healthier lifestyles, and raise revenue for health-related initiatives.
- Registration: Businesses involved in the import, production, or storage of excise goods are required to complete excise tax registration in UAE with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) and must file periodic tax returns.
Implementing the Excise Tax is part of the UAE’s broader strategy to diversify its revenue sources and reduce its reliance on oil revenues.
Excise Tax Rates in the UAE
The UAE has implemented an excise tax on certain products and services, particularly those considered harmful to human health, such as tobacco, energy drinks, and sugary beverages. The UAE excise tax list is set as follows:
- Tobacco Products: A 100% excise tax is imposed on tobacco products while doubling their retail price. This high tax rate aims to discourage tobacco use due to its well-documented health risks.
- Energy Drinks: These beverages are marketed as stimulants for the body and mind and typically contain caffeine, taurine, ginseng, and guarana. The UAE applies a 100% excise tax on energy drinks. It includes any product that can be converted into beverages, such as concentrates, powders, gels, or extracts. This tax doubles the retail price of energy drinks.
- Carbonated Drinks: The excise tax on carbonated beverages includes all aerated drinks except carbonated water. The price is set at 50% of the retail price. This category also covers products intended to be converted into carbonated drinks, such as powders, gels, or extracts.
The UAE has implemented these high excise tax rates as part of a broader strategy to reduce the consumption of harmful products and promote healthier lifestyles among its residents.
How to Calculate Excise Tax in UAE?
The UAE employs two distinct methods for calculating excise tax on specific goods:
Specific Method
The specific method involves applying a fixed tax rate per product unit. This straightforward approach makes the tax amount predictable and easy to administer. For example:
- Cigarettes: A fixed excise tax of AED 0.4 per cigarette.
- Energy Drinks: A tax of AED 0.1 per millilitre.
This method clarifies businesses and consumers by ensuring the tax amount remains consistent regardless of the product’s price.
Ad Valorem Method
The ad valorem method determines excise tax based on the product’s value. This method is typically used for goods where the value fluctuates significantly. For example:
- Luxury Cars: A 50% excise tax on the retail price.
- Jewellery: A 5% tax on the retail value.
The ad valorem method is more complex, requiring an accurate product valuation to determine the taxable amount. This method is often applied to high-value or luxury items whose prices vary widely.
Examples of Excise Tax Calculation in UAE
Let’s examine some examples to better understand the excise tax calculation in UAE using the specific and ad valorem methods.
Specific Method
The specific method applies a fixed tax rate per product unit, making the calculation straightforward.
Example 1: Cigarettes
- Product: A pack of 20 cigarettes
- Excise Tax Rate: AED 0.4 per cigarette
Calculation:
Total Excise Tax = 20 cigarettes × AED 0.4 per cigarette = AED 8
So, the excise tax on a pack of 20 cigarettes would be AED 8, regardless of the pack’s retail price.
Example 2: Energy Drinks
- Product: A 250ml can of energy drink
- Excise Tax Rate: AED 0.1 per millilitre
Calculation:
Total Excise Tax = 250ml × AED 0.1 per ml = AED 25
The excise tax on a 250ml energy drink would be AED 25.
Ad Valorem Method
The ad valorem method calculates the excise tax based on the product’s value, making it a percentage of the retail price.
Example 1: Luxury Car
- Product: A luxury car with a retail price of AED 500,000
- Excise Tax Rate: 50% of the retail price
Calculation:
Total Excise Tax = AED 500,000 × 50% = AED 250,000
The excise tax on the luxury car would be AED 250,000.
Example 2: Jewellery
- Product: A piece of jewellery with a retail price of AED 10,000
- Excise Tax Rate: 5% of the retail price
Calculation:
Total Excise Tax = AED 10,000 × 5% = AED 500
The excise tax on the jewellery would be AED 500.
These examples illustrate how the UAE uses specific and ad valorem methods to calculate excise tax, depending on the nature of the product. The specific method is used for items with a fixed unit measure, while the ad valorem method is applied to goods with variable values.
Challenges in Implementing Excise Tax in the UAE
Implementing the excise tax in the UAE presents key challenges:
- Cross-Border Transactions: Enforcing tax compliance and collecting revenue in cross-border transactions is difficult, requiring robust border controls and international cooperation.
- Impact on SMEs: Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) may struggle with increased costs, needing to balance higher prices or lower profits. Addressing this impact requires careful policy adjustments.
Documents Required for Excise Tax Registration
To complete your excise tax registration, you must provide several key documents to verify your information. The required supporting documents include:
- Passport Copy: For personal identification.
- Emirates ID: This is for proof of residency and identity.
- Trade License: To confirm your business operations in the UAE.
- Other Official Records: Any additional documents that verify your business’s eligibility to conduct activities within the UAE.
Business Details Required for Registration
You will also need to provide specific information about your business, including:
- Your Role: Indicate whether you register as a producer, importer, or another role.
- Details of Excise Goods: Information about the excise goods your business handles.
- Customs Authority Registration: Provide details if applicable.
- GCC TRN: If registered for excise tax in another GCC state, include your Tax Registration Number (TRN).
Make sure that all documents and details are accurate to facilitate a smooth registration process.
Excise Tax Advisory Services in the UAE
Dealing with the complexities of excise tax in the UAE can be challenging. To have smooth compliance and avoid substantial fines, it is important to seek guidance from qualified tax advisors.
At Shuraa Tax, we specialise in excise tax consulting in Dubai. Our expert team is dedicated to helping you understand, calculate, and file your excise taxes with precision. We provide personalised advice to your specific needs, ensuring you stay compliant with all regulations.
For expert support and the intricacies of excise tax, contact us at +971 50 891 2062 or email info@shuraatax.com. Let us help you manage your tax obligations smoothly and efficiently.